Table of Contents
The Mobile Location Protocol is used as a standard protocol for location based services. The main function of MLP is to make possible the inter-operation of application with the location systems themselves.
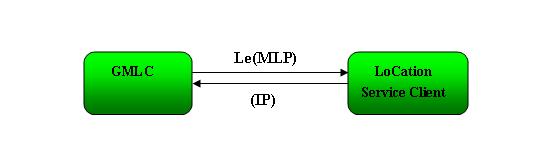
The MLP serves as the interface between a Location Server and a Location Services Client (LCS) (figure 4.1). Possible realizations of a Location Server are GMLC (i.g figure 2.1), which is the location server defined in GSM and UMTS, and the MPC, which is defined in ANSI standards.
It Define a simple and secure access method that allow Internet applications to query location information from a wireless network.
It gives a way of communication to external applications giving enough information about the position, speed, altitude and some other data.
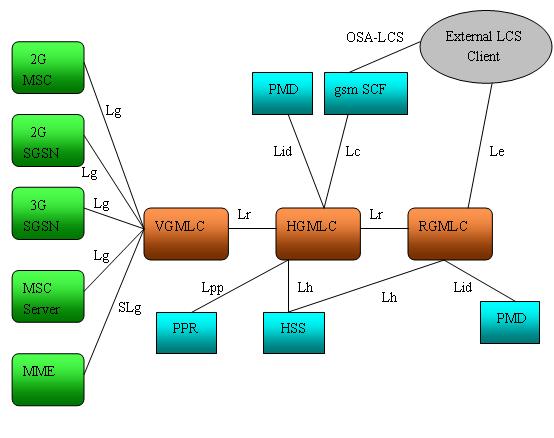
A General arrangement of LCS with inter-GMLC is given by 3GPP, which show that GMLC consists of VGMLC, HGMLC and RGMLC.
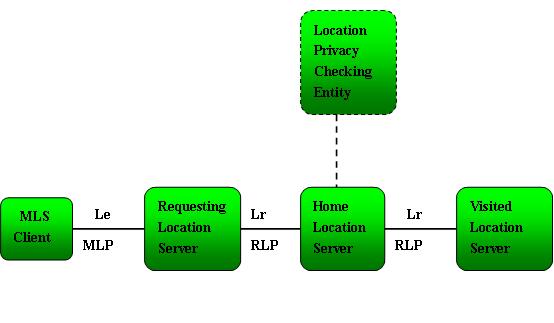
Complying with 3GPP Release 7 LCS Specification [23.271 Rel-7] reference to literature, Open Mobile Alliance (OMA) specified basic structure of LBS services in the OMA Mobile Location Service V1.2[3] which consists of a set of location specification. Specification suggest basic architectural diagram of LBS as seen on figure 3.2. It is more detailed scheme of Location Platform with defined protocols for each interface. Location Privacy Checking Entity is not specified by OMA.
More specifically, the Mobile Location Protocol is used for the communication between the MLS Client and the Requesting Location Server (RGMLC).
MLS client corresponds to the Location Services client (LCS Client) in 3GPP context.
The Location Privacy Checking Entity is responsible for resolving IDs and for privacy checking. In 3GPP context this corresponds to the Privacy Profile Register (PPR). The PPR may be a part of the GMLC.